Web Application Development in Java training
JSP is a powerful technology and it gets even more powerful when used properly!
As mentioned in the previous topic, most web applications are built using an MVC architecture. Most of the time, the controller will be a Java servlet, the model a POJO (Plain Old Java Object) or a JavaBean which exposes methods and the views are JSP.
We saw how to add an attribute to a request in the controller and access it from the JSP using EL and the requestScope object. In the previous example, the attribute was a scalar value. In most large applications, the attribute(s) might be complex object hierarchies and, consequently, it is important that JSP tags be extended to include conditionals, looping constructs and so on.
This is the role of JSTL, the JSP Standard Tags Library.
We will rewrite the Countries/Artists/Songs application to be compliant with the MVC architecture. We will also make sure that views leverage the tags found in JSTL. We will follow the following steps:
- We create three model POJOs: Artist, Country and Song. Those classes have the same attributes as in the database and appropriate getters/setters.
- We import the singleton DatabaseConnection.
- The next step is to create Data Access Objects (DAO) so that our model is decoupled from the underlying database. We also create a new runtime exception, DAOException, to be thrown instead of SQLException in case of problems. Create DAOException, CountryDAO (with a findAll method which returns a list of Countries) and CountryDAOTest.
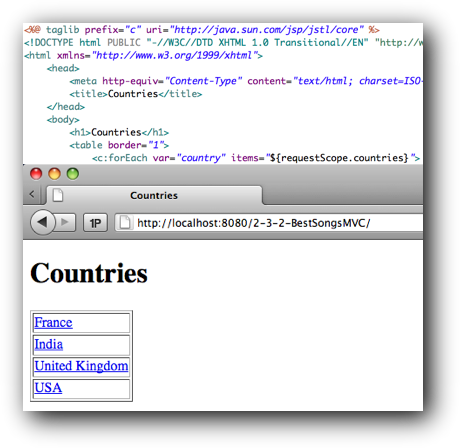
- The next step is to create CountriesController (as a Java Servlet). This controller uses CountryDAO to get a list of all countries, assigns the list as an attribute to the request and selects a view (CountriesView.jsp).
- As the view requires JSTL, it is important that jstl.jar and standard.jar (from the Tomcat installation) be added to the project.
- Finally, the view, CountriesView.jsp, is written.
- <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
- c:catch
- c:choose
- c:forEach
- c:forTokens
- c:if
- c:import
- c:otherwise
- c:out
- c:param
- c:redirect
- c:remove
- c:set
- c:url
- c:when
- Adding AddToCartController (which when given a songid adds that song to the shopping cart belonging to the session) requires that the method findById(int songid) be implemented in SongDAO. For cosmetic reasons, an AddToCartView.jsp is also needed.
- CartController is trivial because it just forwards to CartView.jsp. The shopping cart is accessed through the sessionScope object and, as it is a list of songs, a c:forEach can be used to display them.
- Clearing the cart is left as an exercise…
- Create a tags folder in WEB-INF
- Add a simple footer.tag to it
- Refer to the footer tag from the existing JSP
- Add a header.tag which takes as a parameter a title
- Refer to the header tag from the existing JSP
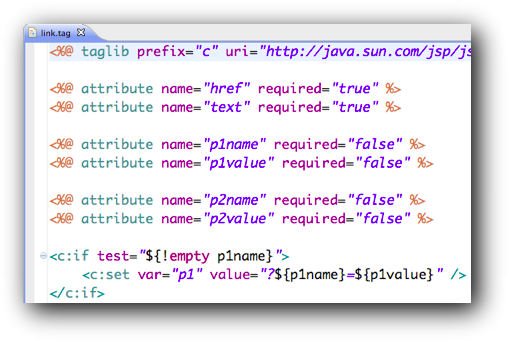
- Finally, create and use a link.tag which makes writing the various HTML links in the web application easier. One possibility is illustrated above.
CountriesView.jsp uses the JSTL Core tag library (taglib) so the following line is needed:
Furthermore, the view will get the list of countries from the requestScope and loop through the countries using the c:forEach tag.
For information, JSTL Core contains the following tags:
Displaying artists…
The next step is to write ArtistsDAO (with a findByCountryid(int countryid) method which returns a list of artists who are from the same country), ArtistsController (which now takes one parameter, the countryid). Interestingly, this means that two views need to be writter, the expected ArtistsView.jsp and ErrorView.jsp in case, for instance, countryid is not valid.
ArtistsView.jsp will, of course, be written using JSTL tags (including, most probably, c:if, to know when to display the list of artists). Accessing a request parameter (which is not the same thing as a request attribute) is done through the param object in JSP.
… and songs + and the rest
To display songs, we need SongDAO (with the findByArtistid(int artistid) method), SongsController (which now takes two parameters: countryid and artistid) and the corresponding view, SongsView.jsp.
The rest is straightforward:
Using custom tags
The standard tag library is very useful as it is but it is also possible to create custom tag libraries with custom tags. For example, we will do the following:
Web Application Development in Java training


Leave a Reply